Plant breeding innovation contributes to sustainably providing sufficient and healthy food supply from plant varieties with improved characteristics.
Over the past 100 years, the world’s population has grown exponentially from 1.75 to today 7.2 billion people, and created an ever-increasing demand for plant based raw materials for food and feed as well as industrial uses.
Yet, while achievements are impressive, in the light of continued population growth and growing worldwide demand for a varied, high quality food supply, further progress in plant breeding innovation is of extreme importance.
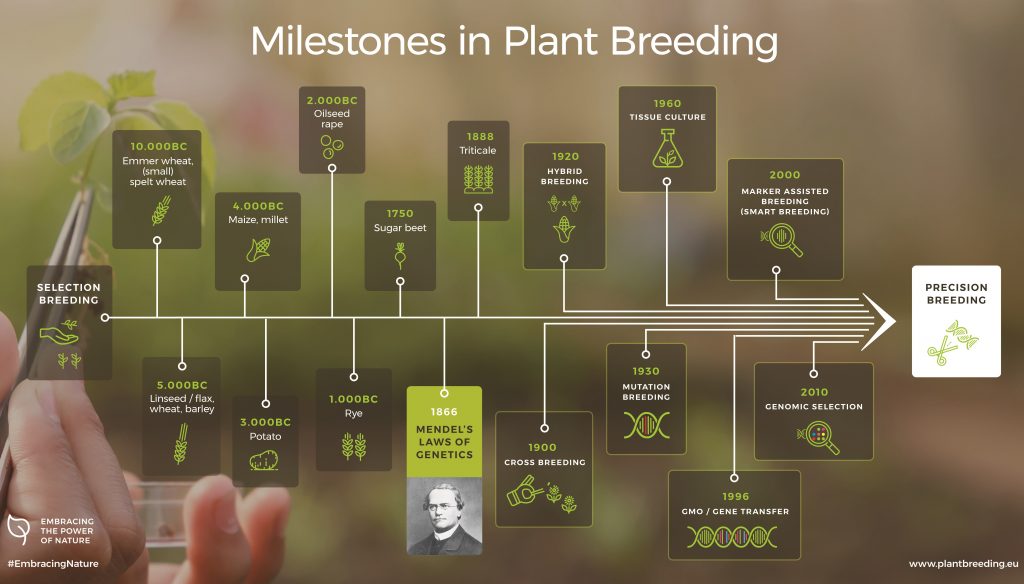
Plant domestication started some 10,000 years ago by farmers who selected the best performing plants in a field. However, it wasn’t until the discovery of Mendel’s laws of heredity in the nineteenth century that plant breeding moved from being an art to a science. The result was specialised farmer/breeders emerged, thereby building a business concept on their efforts.
From that point on, scientific breakthroughs in agricultural and biological sciences have accelerated. With an increased understanding of plant biology and plant genes, plant breeders have constantly improved their breeding tools to include a wide variety of breeding methods. The development of newer plant breeding methods has not led to a complete replacement of the older ones. Depending on the problems plant breeders must solve, they must be able to choose the tools that enable them to reach their breeding goals in the most efficient and specific way.
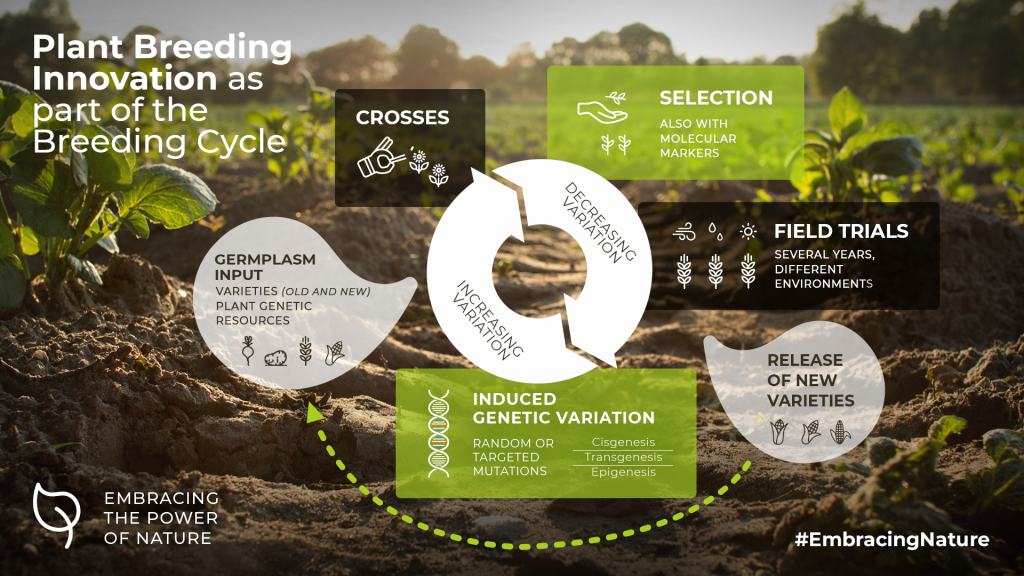
Genetic variation is the “Fuel” of Plant Breeding
Like evolution itself plant breeding depends upon genetic variability within crops and their relatives as a basis for developing new plant varieties with improved characteristics. Conventional plant breeding methods, transgenesis or newer plant breeding methods are all essential components of the plant breeders’ toolbox. By building on the mechanisms created by nature, the latest innovations in plant breeding methods simply achieve the relevant breeding results in less time and with greater precision.
Euroseeds is therefore of the opinion that plant varieties developed using the latest breeding methods should not be subject to any additional regulations if they could have been produced through earlier breeding methods, or might also have been obtained from natural processes without human intervention.
The efficient and targeted development of improved plant varieties is important to fight new plant pests, insects or diseases. These can be devastating to crops and lead to huge pre-harvest losses. Other plant varieties provide quality improvements, such as better taste (e.g. in fruits and vegetables), processing advantages or nutritional enhancements, such as desirable proteins or lower saturated fats.
In this way, plant breeding innovation contributes to providing sufficient and healthy food supply from plant varieties with improved characteristics.